광폭형 볼 밸브와 일체형 볼 밸브는 모두 파이프라인에서 유체의 흐름을 제어하는 데 사용되는 볼 밸브의 종류입니다.
와이드바디 볼 밸브와 싱글피스 볼 밸브는 모두 분할형 바디 디자인과 달리 일체형 바디 디자인을 특징으로 합니다. 이는 밸브 바디가 분할된 2피스 및 3피스 볼 밸브와는 다른 점입니다.
내부 나사산이 있는 광폭형 볼 밸브의 경우, 밸브 본체는 원형 또는 육각형 봉재 또는 단조 부품을 사용하여 제작됩니다. 볼 코어는 직경이 줄어든 형태로 설계되었으며 밸브 본체의 한쪽 면에서 삽입됩니다. 판막 본체는 내부 역류 방지 구조를 갖추고 있습니다. 본체 입구와 출구 양쪽에는 평평한 표면이 가공되어 있어 볼 밸브 조립이 용이하고 배관 설치 시 렌치를 사용할 수 있습니다.
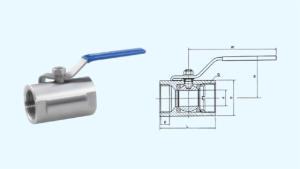
와이드바디 볼 밸브 볼 밸브의 경우, 스템 스터핑 박스가 비교적 얕고 내부 패킹 용량이 제한적이어서 스템의 밀봉 성능이 보통 수준입니다. 따라서 이러한 밸브는 저압 유체에 더 적합합니다. 반면, 2피스 및 3피스 볼 밸브는 고압 유체에 안정적인 밀봉을 제공하는 스템 스터핑 박스 구조를 특징으로 합니다.
플랜지형 광폭 볼 밸브의 구조는 기본적으로 내부 나사식 광폭 볼 밸브의 구조와 동일합니다. 일반적으로 플랜지는 나사식 체결구를 통해 중간 밸브 본체에 연결되지만, 일부 설계에서는 단조 일체형 구조를 사용하기도 합니다.
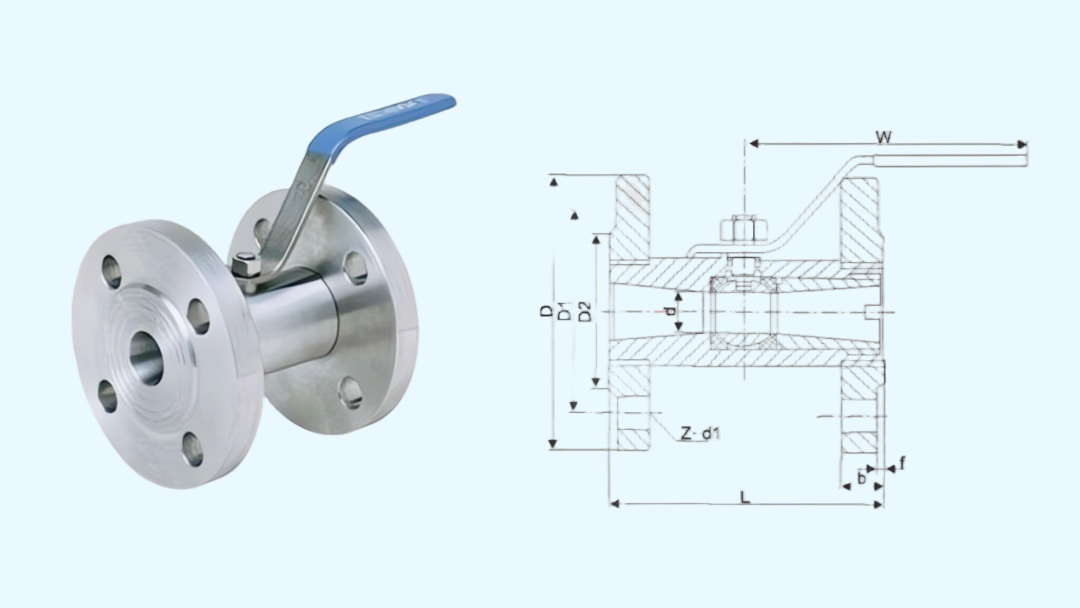
외부 나사산이 있는 광폭형 볼 밸브는 유니온형 구조를 사용할 수 있습니다. 이 구조에서 유니온은 파이프라인에 직접 용접되어 밸브 본체의 외부 나사산에 연결됩니다. 이러한 설계는 파이프라인에 별도의 유니온을 설치할 필요 없이 밸브 유지 보수 또는 교체 시 쉽게 분해 및 재조립할 수 있도록 합니다.
일체형 내나사식 볼 밸브와 일체형 플랜지 볼 밸브의 밸브 본체는 주조 공정을 이용하여 제작되며, 볼 코어는 직경이 축소된 형태로 설계되었습니다. 스템에는 내부 역류 방지 구조가 적용되어 있습니다. 일체형 내나사식 볼 밸브의 입구와 출구 끝단은 기존의 내나사식 밸브와 유사하게 육각형 형상으로 되어 있어 렌치 조작이 용이하고 설치가 안전합니다.
일체형 플랜지 볼 밸브는 플랜지와 밸브 본체가 하나의 단위로 주조되므로, 광폭형 플랜지 볼 밸브처럼 플랜지를 별도로 가공하고 조립할 필요가 없습니다. 이러한 방식은 비용을 절감하고 제조 공정을 간소화합니다.
일체형 웨이퍼형 볼 밸브는 밸브 본체 길이가 짧아 공간이 제한된 배관에 더욱 적합합니다.
광폭형 볼 밸브와 일체형 볼 밸브는 모두 직경이 작은 볼 디자인을 사용하기 때문에 2피스 및 3피스 볼 밸브에 비해 유량 저항이 더 높습니다.
주요 차이점은 다음과 같습니다.
밸브 본체 제조 공정
● 광폭형 볼 밸브는 본체에 원형 또는 육각형 봉재를 사용하며, 일반적으로 단조 방식으로 제작됩니다. 이는 모래 구멍, 수축 공동 또는 기공과 같은 주조 결함을 방지하고 더 큰 가공 여유를 제공합니다.
● 일체형 볼 밸브는 정밀 주조 방식으로 제작되어 가공 여유가 더 작습니다.
파이프라인 연결 방법
● 광폭형 볼 밸브는 내부 나사산, 플랜지, 페룰 연결부 또는 외부 나사산 유니온형 연결부를 사용하여 연결할 수 있으며, 유니온형 연결부는 파이프라인에 직접 용접할 수 있습니다.
● 일체형 볼 밸브는 일반적으로 내부 나사산, 플랜지 또는 웨이퍼형 연결부를 사용하여 연결됩니다.
비용
● 탄소강 밸브의 경우 두 종류 간의 가격 차이는 미미합니다.
● 단조 304 또는 316 스테인리스강의 경우, 광폭형 볼 밸브는 일체형 볼 밸브보다 가격이 약 두 배 더 비쌉니다.
스템 스터핑 박스 구조
● 내부 나사산, 외부 나사산 및 플랜지형 광폭 볼 밸브의 경우, 스템 스터핑 박스가 비교적 얕고 패킹 용량이 제한적입니다. 따라서 빈번한 작동 시 스템에서 누출이 발생할 수 있습니다. 개선된 밸브 본체 설계는 더 많은 패킹을 수용할 수 있는 높이가 있는 스터핑 박스를 특징으로 하여 스템에서의 유체 누출을 방지합니다.
● 일체형 내부 나사식 볼 밸브의 스터핑 박스는 상대적으로 얕습니다. 일체형 플랜지 볼 밸브의 경우, 스터핑 박스가 더 높아서 내부 나사식 버전보다 더 많은 패킹을 수용할 수 있어 스템 부분의 밀봉 성능이 향상됩니다.
절연 볼 밸브 적용 분야
● 단열 개조를 위해 플랜지형 광폭 볼 밸브 대신 일체형 플랜지 볼 밸브가 사용됩니다.
이전 :
블라인드 플레이트 밸브다음 :
웨지 게이트 밸브 설계 및 밀봉 원리